Introduction
A Geographic Information System (GIS) is a technology for managing geographic, or spatial, data. It is an integrated set of hardware and software tools used for the capture, storage, analysis and display of geographic data. GIS technology integrates common database operations such as query and statistical analysis with the visualisation and geographic analysis benefits offered by maps and charts.There is no single definition of a GIS. Definitions often focus on specific areas and disciplines and the context in which it is used. All definitions recognise the spatial component of the data. Some of the broadly accepted definitions of GIS include:
“a geographic information system is a special case of information systems where the database consists of observations on spatially distributed features, activities or events, which are definable in space as points, lines, or areas. A geographic information system manipulates data about these points, lines, and areas to retrieve data for ad hoc queries and analyses“[1]
“a powerful set of tools for the storing and retrieving at will, transforming and displaying spatial data from the
real world for a particular set of purposes“[2]
Some recent definitions include
[3]:
- a container of maps in digital form
- a computerized tool for solving geographic problems
- a spatial decision support system
- a tool for performing operations on geographic data that are too tedious or expensive or inaccurate if performed by hand
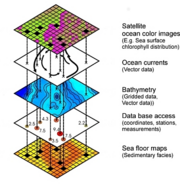
A more comprehensive and easy way to define a GIS is to look at the nature of
the system and how it works with thematic layers. A GIS organises and stores
information about the real world as a collection of thematic layers that are
linked by geography. This way is possible to analyze the spatial characteristics
of the data. A GIS can answer questions about:
- Location: "What is at ...?"
- Trends: "What has happened since ...?"
- Patterns: "What spatial patterns exist ...?"
- Modelling: "What if ...?"